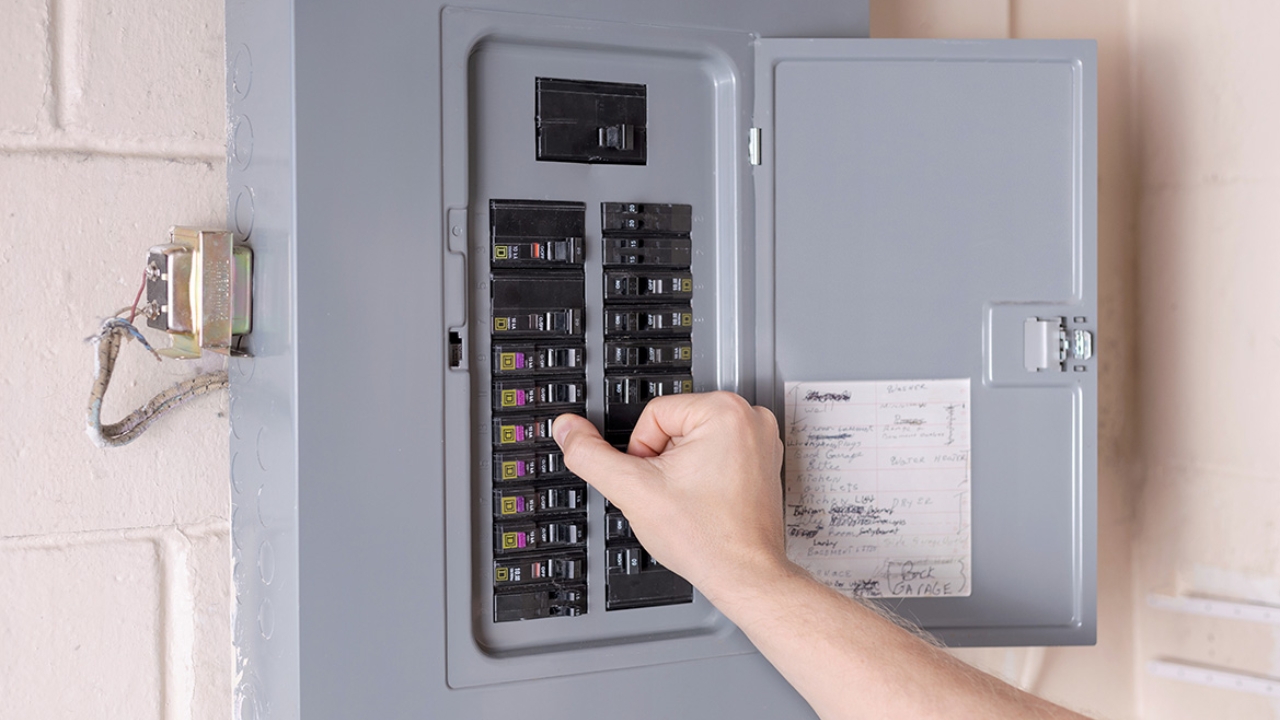
Understanding what differentiates circuit breaker vs electrical panel is important for the maintenance of an effective and safe electrical system. Although people confuse one for the other, they don’t serve the same purpose. In this article, we’ll go into full details regarding what differentiates both of them. But first, what do they mean?
What is a Circuit Breaker?
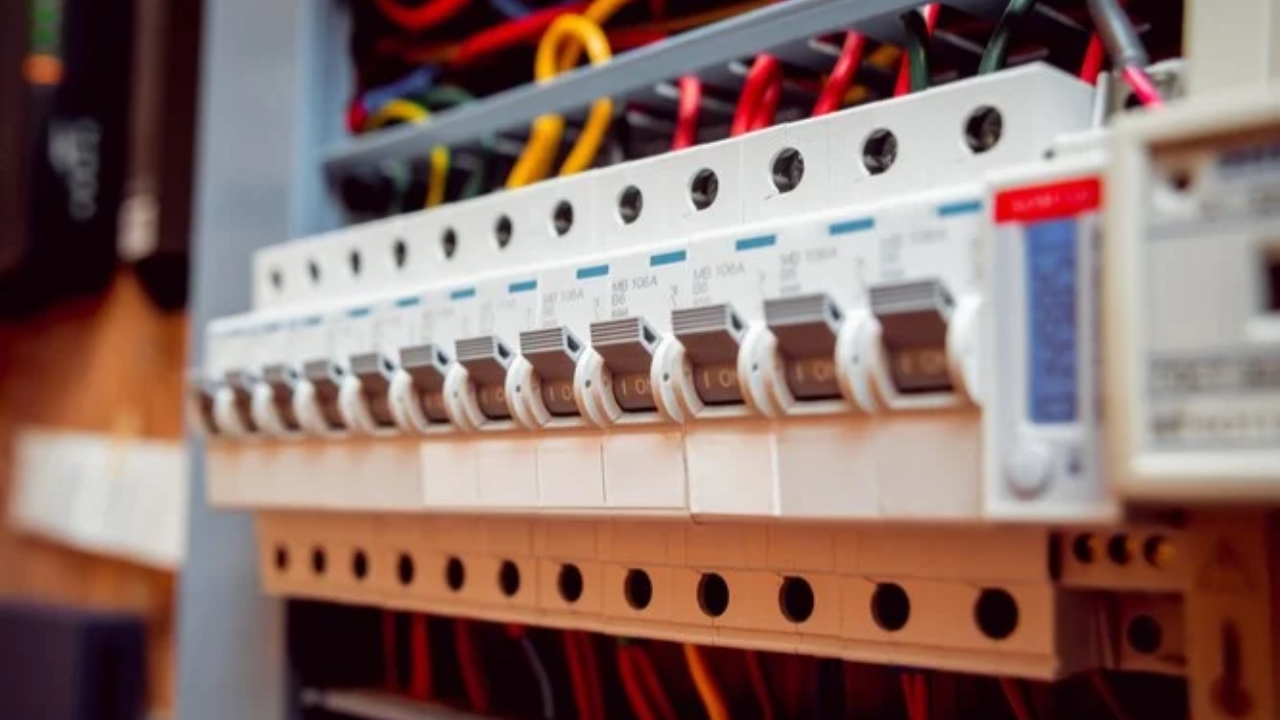

Circuit breakers are safety devices that provide protection for electrical circuits from possible damage that can result from short circuits or overloads. Whenever it detects an abnormal flow of current, the circuit breaker trips, thereby preventing damage to the equipment as well as fires. With this, you are enhancing the safety of your household, preventing your wiring and appliances, and also preventing electrical fires.
What is an Electrical Panel?
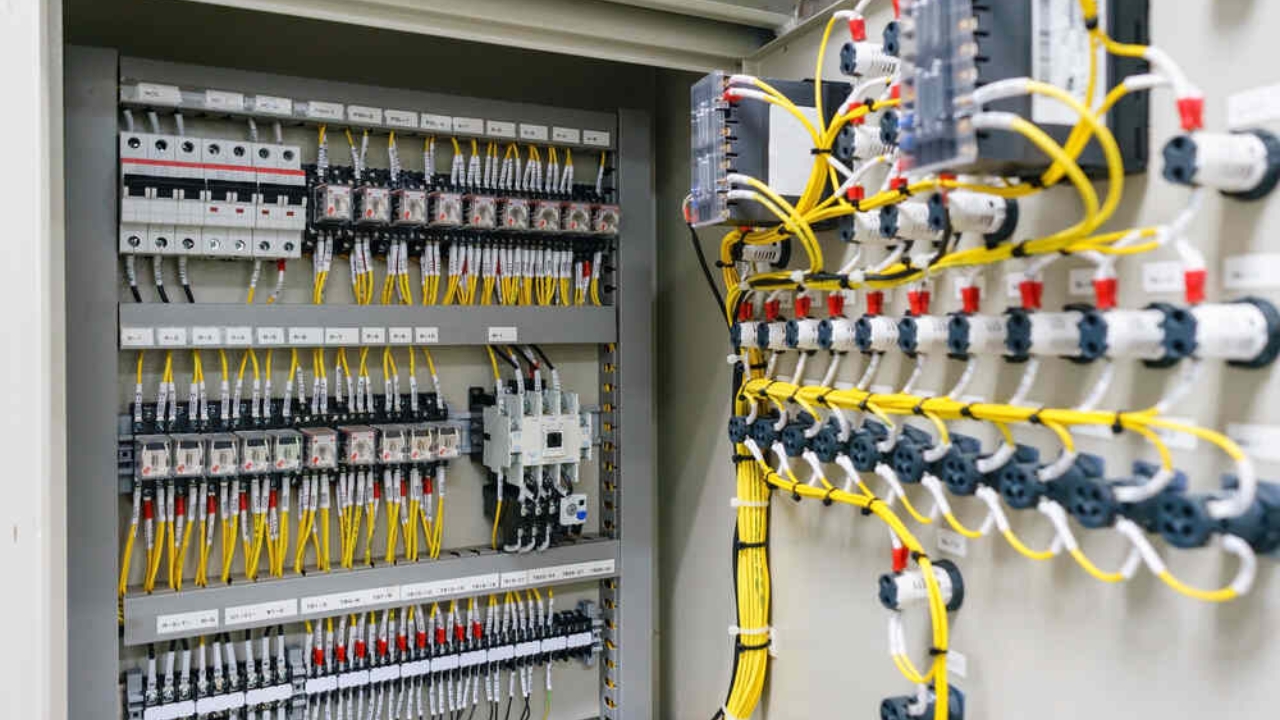
Electrical panels, which also means distribution boards or breaker boxes, encloses many circuit breakers. They serve as the main hub for the distribution of electrical power onto several circuits present in a particular building. Electrical panels provide you with safety by organizing the distribution of power and controlling your electrical system from a central location.
Circuit Breaker vs Electrical Panel: The Differences
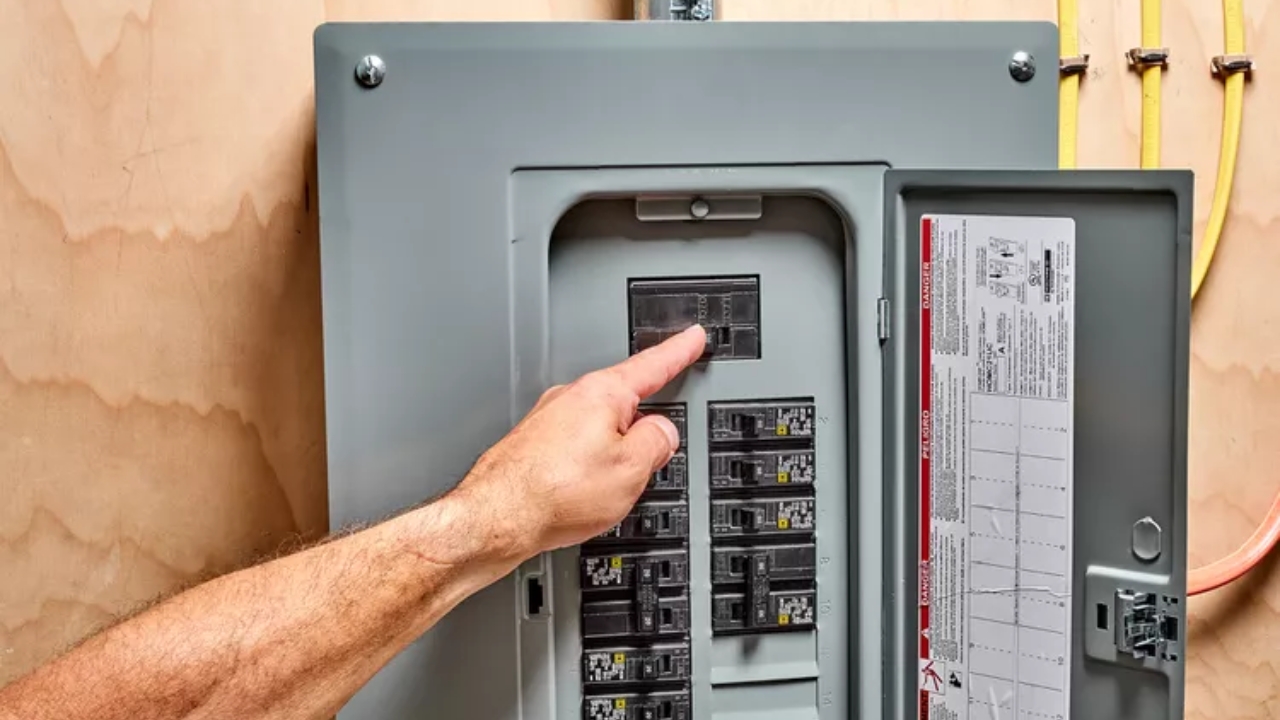

Every electrical system features electrical panels and circuit breakers. These components help your electrical system to function as expected. Now, let’s discuss the differences between these two components in terms of their functions, types, applications, and other aspects.
Types
Circuit breakers: There are different types of circuit breakers with each designed to carry out certain functions. The miniature circuit breaker (MCB) is commonly used in residential apartments. This type of circuit breaker protects your electrical system from issues like short circuits and overloads.
Another common circuit breaker type is the Molded Cases Circuit Breaker (MCCB). You install this type of circuit breaker in industrial or commercial settings where there are higher current ratings. Other circuit breakers include the Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters and Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters, also known as AFCI and GFCI respectively. While AFCI offers protection against electrical fires that may result from arc faults, GFCI helps to prevent shock hazards from occurring in wet areas. Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) detects earth faults on time and prevents them from occurring.
Electrical Panels: When it comes to types, electrical panels are available based on your electrical distribution needs. There are the main breaker panels and the subpanels. While the main breaker is the primary control hub for your electrical system, the subpanels expand their capacity to certain areas of your property. If you are living in older homes, you may find fuse boxes still in use, although they are now outdated.
It is important you use transfer switch panels in areas where you need backup generators. These panels enable smooth power transitions. However, you can use load centers in residential properties to ensure proper distribution of basic circuits.
Purpose
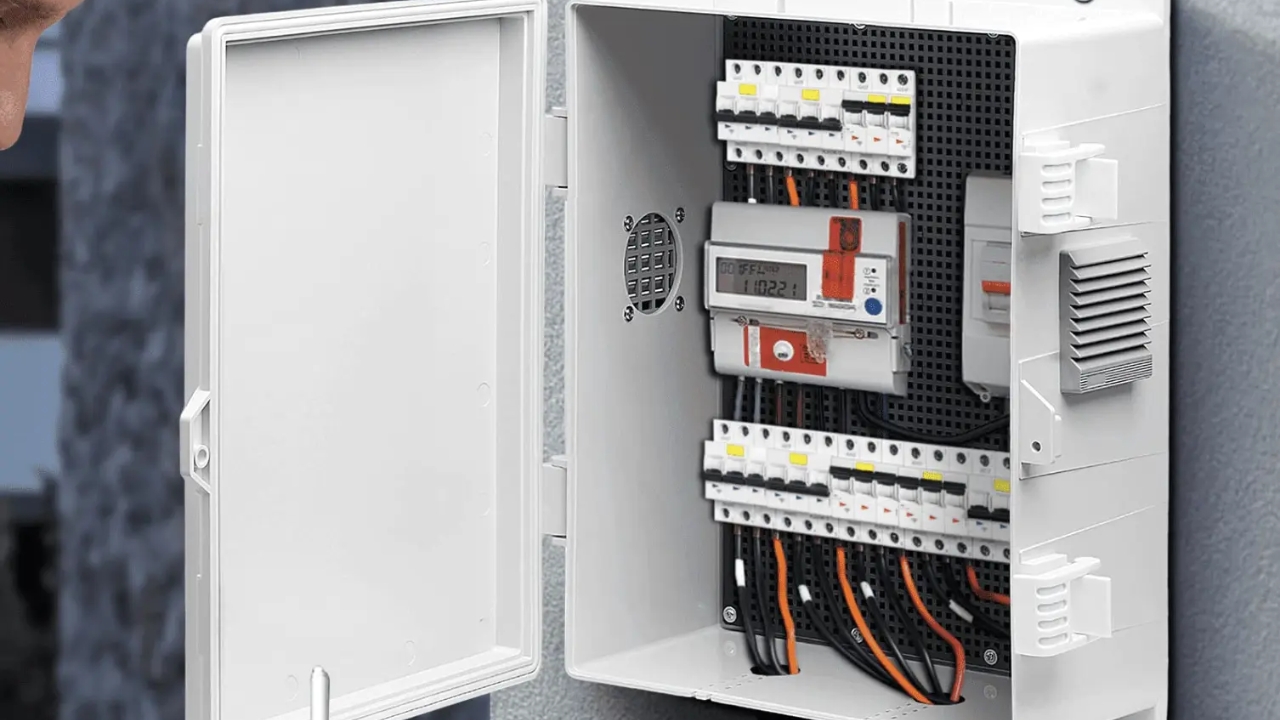

Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker’s role is to disrupt the flow of power in the event of short circuits or overloads. Short circuits or overloads can cause further damage to appliances. However, a circuit breaker prevents this from happening and as well minimizes the possible risk of electrical fire. Therefore, you can consider a circuit breaker as a barrier between electrical appliances and dangerous electrical surges.
Electrical panel: The main purpose of an electrical panel in your electrical system is to distribute electricity within your property. This electrical component discharges power from the main supply into different circuits while ensuring there is adequate power in different areas of your building.
Functionality
Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker functions in such a way that it easily identifies any irregularities in the flow of current. If there is a short circuit or overload, this breaker interrupts power to prevent possible damages. You only need to reset your circuit breaker manually. This makes it different from fuses that require you to replace them.
Electrical panel: You can see an electrical panel as the organizational framework for your electrical system. This panel uses an individual circuit to distribute power. Also, they are the central control hub for separating certain areas. During maintenance, your electrical panel allows de-energizing of certain parts of the wiring system to ensure safety.
Installation Areas
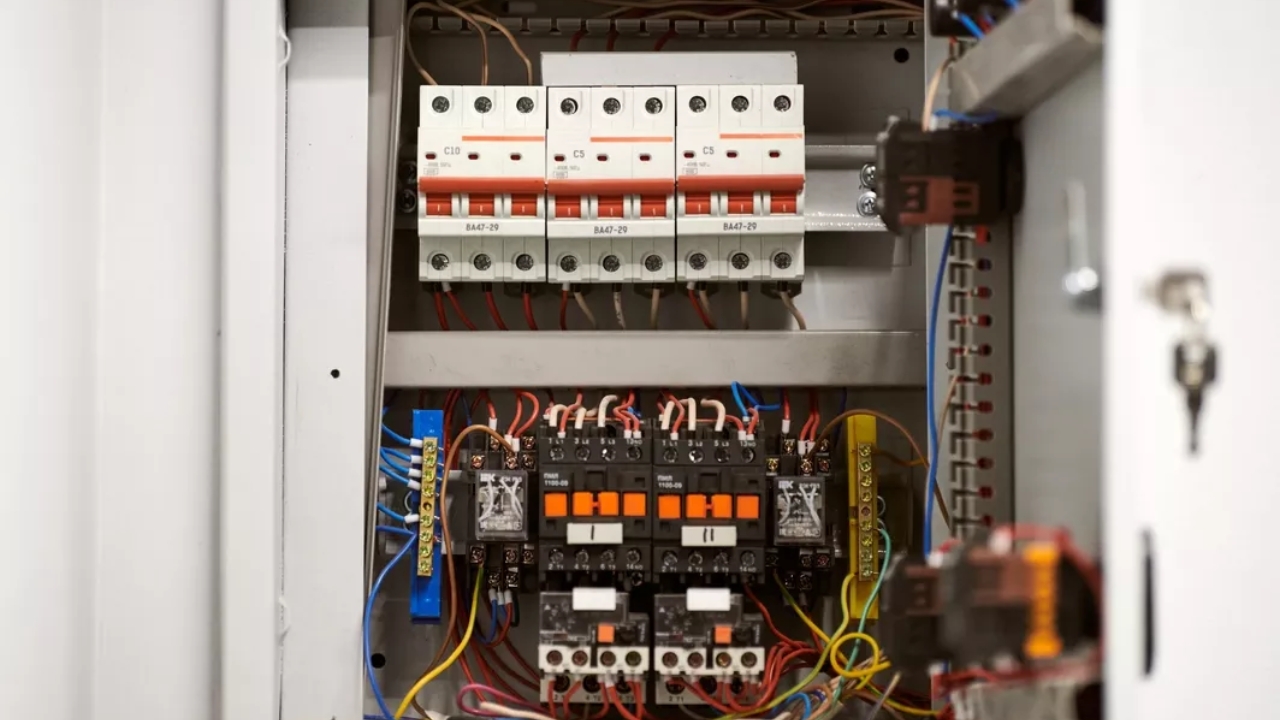
Circuit breaker: You should install a circuit breaker within your electrical panel, ensuring that each connects properly to a particular circuit. For industrial settings, you can integrate dedicated breaker enclosures to protect your equipment. During installation, you must ensure the breaker is suitable with the capacity of the circuit and application requirement.
Electrical panel: The best area to install your electrical panel is where you can easily access. For example, garages, basements, and utility rooms are ideal areas to install your electrical panel. During installation, you must secure the panel that connects incoming power lines. The installation procedure is a complex one with the possibility of hazards. Therefore, you should allow a professional to handle the installation.
Maintenance
Circuit breakers: Regular inspection is necessary for maintaining circuit breakers. This helps to detect visible or potential damage or losses connections on time. Manufacturers always recommend regular testing to evaluate breaker’s response to faults. You may need to replace your circuit breaker if you notice constant tripping without any reasons.
Electrical panels: You need to inspect your electrical panels thoroughly to detect any case of moisture intrusion or overheating. Problems like this can cause malfunction or electrical fire. Ensure you check and tighten all connections to prevent arcing. Once you notice outdated components, replace immediately..
Discoloration or burning odors are signs of internal issues which requires immediate replacement of repairs of some components. For your panel servicing, ensure you hire a professional.
Cost
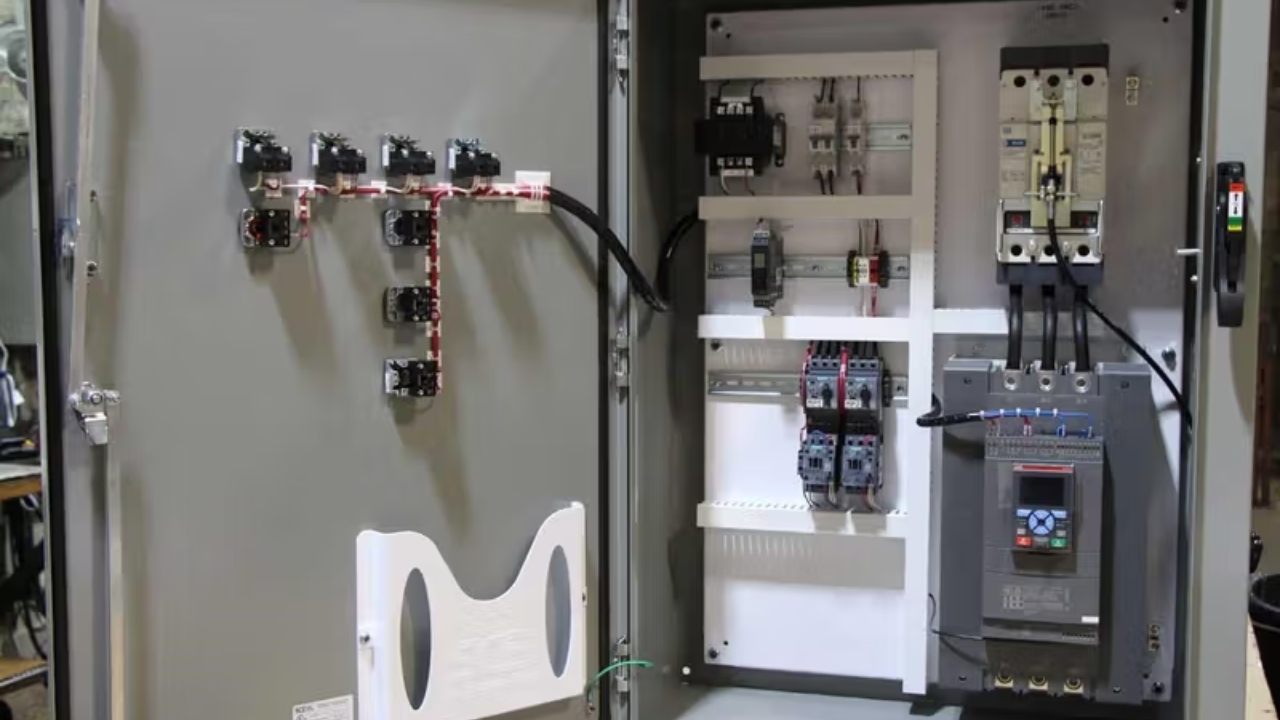

Circuit breaker: The type and capacity of a circuit breaker determine its cost. For standard residential breakers, make sure you budget from $10 to $100. You spend more of your money buying AFCI or GFCI. You can easily replace a breaker. When replacing, turn off the main power of the other panel and get rid of the damaged breaker and put in a new one. Regardless of how simple it sounds, ensure you take precautions to avoid accidents.
Electrical panel: Electrical panels are usually very expensive. Your budget for an electrical panel should range between $600 and $2000 either for upgrades or new installations.
Replacing an electrical panel takes a lot of time and effort as it requires you to reroute the writing and disconnect circuits. When the capacity of your existing panels can’t handle your appliances anymore, you should consider upgrading .
Safety

Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker disconnects power when there is an electrical fault. This serves a form of protection against equipment damage and electrical fires. GFCI and AFCI require proper testing to maintain good performance in places exposed to moisture.
Electrical panel: Electrical panels provide safety by preventing the risks of shock. Therefore, you should install them in accessible areas. You should label all circuits for easier identification in cases of emergency. For safety and emergency purposes, do not obstruct your panels with anything.
Lifespan
Circuit Breaker: In general, the lifespan of a circuit breaker is between 15 and 30 years. However, this still depends on environmental conditions and usage. Unfavorable conditions such as extreme temperatures, frequent tripping, and humidity can reduce their lifespan. You can extend the lifespan of your circuit breaker by ensuring regular inspection and maintenance.
Electrical panel: For electrical panels, expect a life span ranging between 25 and 40 years. However, factors like maintenance and electrical load can affect their lifespan. If you are using older panels you may need to replace them for higher electrical load.
Size and Capacity
Circuit breaker: Circuit breakers have different ratings based on their amperes. Their amperes (amps) indicate how much current they can handle. If you are using a circuit breaker for your home, you can go for 15A to 50A. These amperes are ideal for home appliances. You need a circuit breaker with more amps for commercial and industrial applications.
Electrical panel: Electrical panels are available in different sizes based on their total amperage capacity and the number of breaker slots they have. For residential purposes, you can use panels within 100A and 200A. You can use electrical panels with more than 400A for commercial or industrial spaces. It is crucial you choose the right panel size that can align with your electrical needs.
Usage Conditions
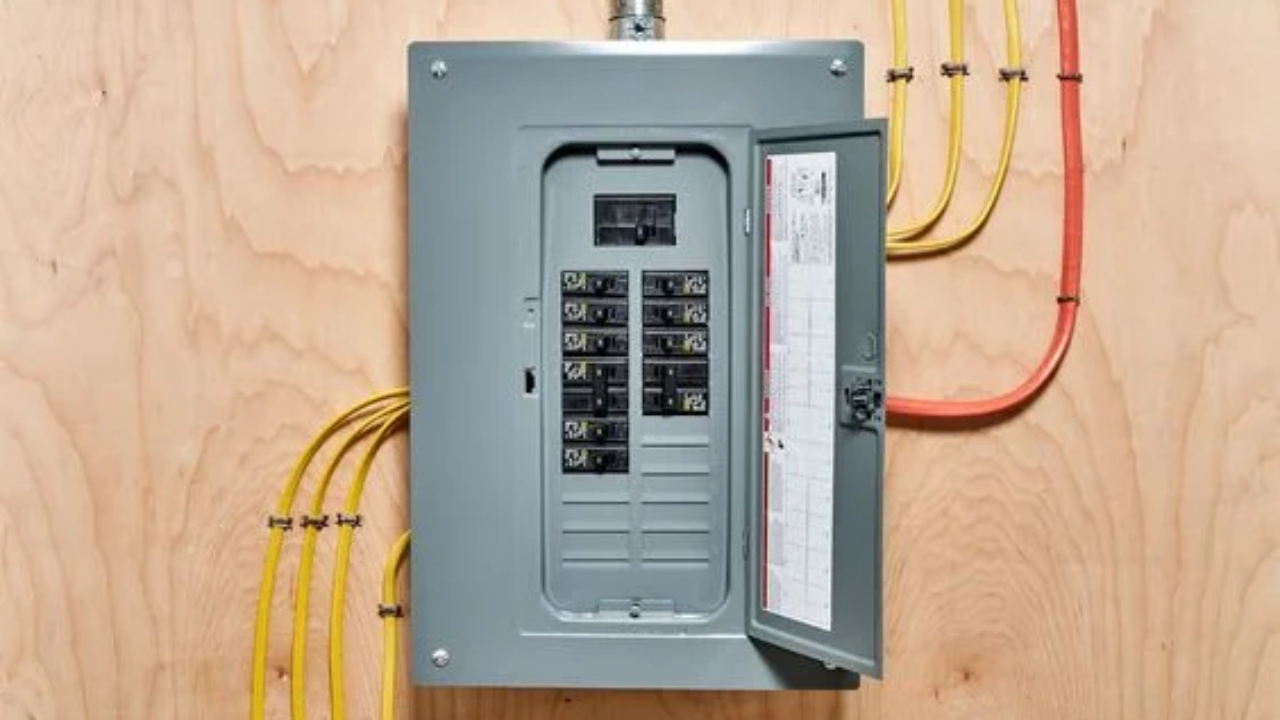

Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker is flexible as you can use it in different contexts. For example, you can use it for home appliances and industrial machinery. Special circuit breakers like GFCI are ideal for use in moisture-prone locations. On the other hand, AFCI is useful in some specific areas to prevent electrical fires.
Electrical panel: You can use an electrical panel to distribute power in your entire property. If you use it in your building, it ensures your electricity needs are met. In commercial spaces, you can use electrical panels in heavy equipment and panel control lighting. A good number of industrial devices depend on electrical panels for power supply.
Issues and Repairs
Circuit breaker: Faulty appliances or electrical overloads cause frequent tripping. You can choose high-quality breakers that trip only when necessary. Breakers that don’t trip when necessary may have mechanical failure. You might need to replace your circuit breaker if you notice this.
Electrical panel: Common issues associated with electrical panels include overheating l, poor installation, and corrosion. If your panel is obsolete, it might pose a potential risk. Therefore, it is important you upgrade old panels or replace them entirely. However, ensure you get a professional to handle any upgrade or replacement.
Applications
Circuit Breaker: A circuit breaker protects circuits that power your appliances. You can use them for both residential and commercial purposes. In commercial applications, you need to choose the right rating for your circuit breaker since it will be handling higher electrical load. Common applications of circuit breakers include specialized equipment, HVAC systems, and industrial machinery.
Electrical panel: This panel distributes electricity for different settings. They are available in different sizes and as such, you can use them in different applications. Common applications of electrical panels include homes, offices, manufacturing sites, warehouses, and retail spaces. For industrial purposes, electrical panels handle equipment with high voltage and offer support for backup systems like solar installation systems or generators.
Conclusion

To ensure the smooth operation of your electrical system, it is important you know the difference between electrical panels and circuit breakers. As much as these components both ensure electrical safety, they are different as regards their functions, installation procedure, and applications.
Circuit breakers interrupt faulty currents to protect electrical failure while electrical panels distribute electricity in an entire building. Both electrical components are used in residential, industrial, and commercial settings. To achieve efficient electrical solutions, you should work with reliable manufacturers such as kdmsteel.com. Also, it is advisable to allow a professional to help you install your circuit breaker and electrical panel to ensure smooth functioning and safety.



