When you prioritize safety, fire prevention and environmental protection, dry-type transformers are an irreplaceable choice. Correctly selecting the size of the transformer is crucial for engineering practice, economic benefits, and safety. This article discusses the importance and impact of transformer size and how the size can be matched to your industrial needs. Hope this article can help you choose the appropriate size of dry type transformers.
What are Dry Type Transformers?
A dry type transformer is a type of power transformer that does not use liquids such as mineral oil or silicone oil as insulating and cooling media. The core and windings inside its equipment are directly exposed to the air or encapsulated in solid insulating materials. Dry-type transformers mainly rely on air convection, forced air cooling or heat conduction of solid materials for heat dissipation.
The design without flammable liquids endows it with extremely high safety and fire resistance. The equipment has good electrical performance and can be easily kept. It is also widely installed in commercial buildings, residences, factories and other fields.
Importance of Dry Type Transformer Sizes
Dry type transformer size is usually the materialized result of a multi-factor game involving materials, capacity, voltage, insulation and temperature rise limitations.
If you need a larger KVA rated capacity, it also means that the equipment requires more copper and iron cores, which will directly increase the volume of the core components. Moreover, the size of the dry type transformer is directly related to the design of the heat dissipation channels, such as the winding spacing and the opening ratio of the casing. The insulation safety distance and mechanical strength of dry-type transformers both require a certain structural volume to be guaranteed.
Besides the above factors, the size of dry type transformers also affects short-circuit impedance values, heat dissipation and overload capacity, losses and energy efficiency. The fire safety distance, the maintainability and service life of the equipment, and the installation cost will also be affected by the dry type transformer size.
Therefore, dry type transformer size is important because it is a parameter jointly determined by electrical requirements, physical limitations, engineering practice and economic benefits. If you choose the proper size, it means that your project has achieved the best balance in terms of technology, safety and economy.
Standard Dry Type Transformer Sizes
Industry Standards Specifications
Standard dry type transformer sizes are usually subject to the design boundaries and performance requirements stipulated by National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and International Electrotechnical Commission(IEC). These requirements do not directly stipulate the common dry type transformer size, but rather indirectly frame the minimum possible sizes of transformers through some performance requirements.
The standard specifies the standards for electrical insulation and safety distance of transformers, temperature rise limits and heat dissipation, safety protection grades and types of enclosures.
Among them, electrical insulation and safety distance are the most direct and rigid influences on the size. The standard specifies in detail the electrical clearance and creepage distance according to the voltage level of the transformer (0.4kV,10kV,35kV).
It also specifies in detail the maximum allowable temperature rise limit for windings under different insulation classes, such as F class and H class. If you want to make sure that the temperature rise does not exceed the standard, the transformer must have sufficient heat dissipation surface area. Besides, the fire resistance rating and IP rating of the transformer may slightly affect the thickness and volume of the casing.
Adhering to these standards can guarantee a certain level of quality, safety and reliability of the transformer. And it can operate normally in the power system as you expect.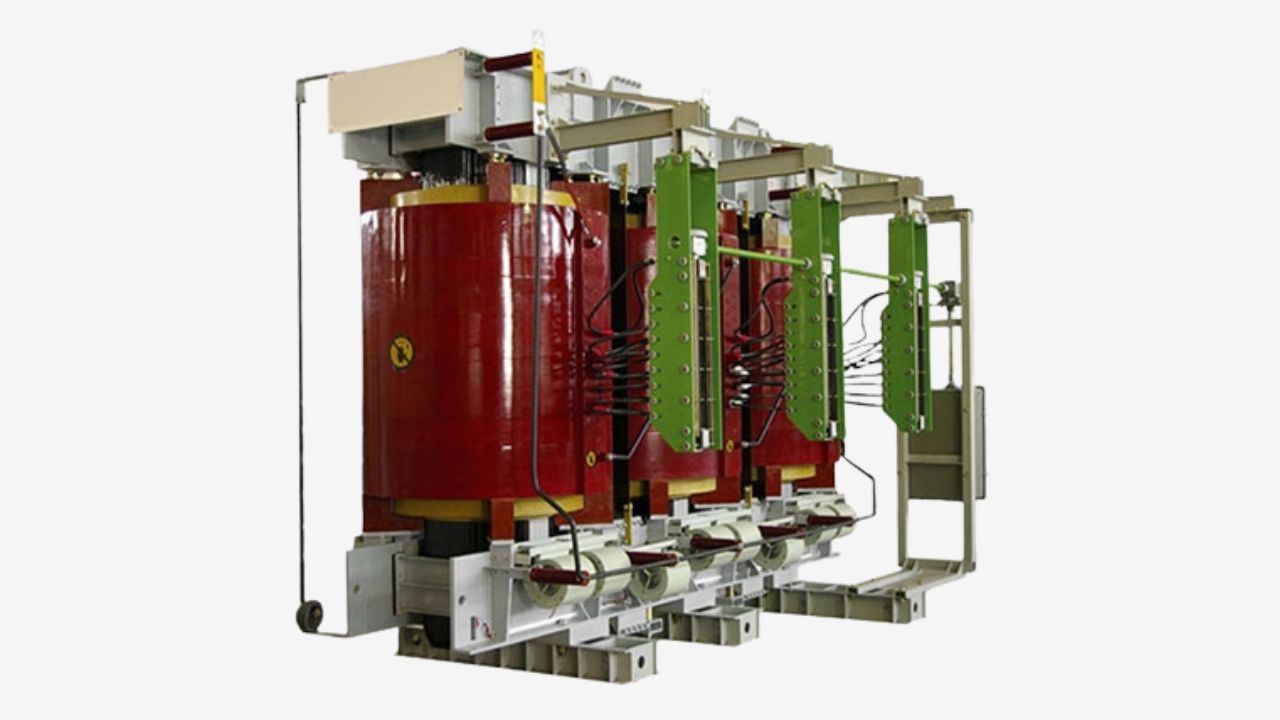
Transformer KVA Ratings
Within the range of variables specified by the standard, the KVA rating is the most significant variable that affects the continuous and systematic changes in size, and its impact on size and transformer function is also fundamental.
If you want to transmit greater power, the transformer needs a larger core cross-sectional area. The height and width of the core window directly determine the core frame size of the transformer. As the KVA keeps increasing, the overall diameter and height of the transformer winding will also increase.
As the KVA increases, your cooling requirements will also rise sharply. You must further optimize the heat dissipation structure of the dry type transformer, such as increasing the number and width of the air channels, which will also further increase the volume of your transformer.
Usually, the common sizes for transformateur monophasé applications range from 1.5KVA to 333KVA. Three phase dry type transformer sizes typically range from 15KVA to 2000KVA. Dry type transformers produced in accordance with standardized KVA ratings can meet your diverse power usage requirements.
Overall, the KVA level is mainly determined by your connection load and expansion requirements. It is usually advisable to choose a transformer that is one grade higher than your total load, which is convenient for future expansion and can better prevent overload.
Influence Factors of Dry Type Transformer Sizes
The dry type transformer size is the final manifestation of the balance and physical constraints of various internal factors. The following provides a detailed explanation of how the cooling method of the transformer, insulating materials and technologies, and winding structure affect the dry type transformer size.
Cooling Method
The cooling method determines the efficiency of heat dissipation from the transformer, which is the most direct factor affecting the dry type transformer size, especially its height and airway design. Cooling methods typically include two types: natural air cooling (AN) and forced air cooling (AF).
If you choose a transformer cooled by natural air, the transformer must be designed with sufficient and smooth heat dissipation air channels. This also means that the transformer needs a greater winding height and a larger winding spacing. Therefore, under the same capacity, transformers cooled by AN are usually the largest in volume and have the most significant height.
If you use a transformateur with forced air cooling, this type of transformer allows for a reduction in the size and number of heat dissipation airways, achieving a compact design. Its heat dissipation efficiency and overload tolerance can both be improved by 30% to 50%. Compared with AF transformers, under the same rated capacity, the volume of AF transformers is usually 15% to 30% smaller.
Although its size has decreased, due to its cooling method, it requires the integration of fans and temperature control systems. And you also need to take into account the installation and maintenance space of the fan, as well as additional power supply and noise. This also increases the complexity of your transformer.
Insulation Technologies
The insulation system determines the electrical safety, environmental tolerance and heat conduction efficiency of the transformer. According to the insulation manufacturing process, it can be classified into cast resin transformers(CRT) and vacuum pressure impregnated(VPI) transformers.
Cast resin transformers use a resin mixture to pour the windings in a vacuum mold and then allow it to cure. This results in a solid insulator. These transformers have a high structural rigidity and extremely high mechanical strength, reducing the need for internal support components and improving the utilization of internal space.
However, resin is not conducive to heat dissipation, so the pouring thickness needs to be uniform and air passages need to be reserved in the pouring mold to ultimately form an integrated heat dissipation channel.
The key to optimizing the size of resin cast transformers lies in balancing the insulation thickness, mechanical strength and heat dissipation requirements. If the transformer adopts a more advanced thin insulation process, it can help you achieve a more compact size.
The VPI transformer is mainly achieved by subjecting the windings to multiple processes of vacuum drying, impregnation with insulating paint, and curing. This type of transformer has good heat dissipation performance.
However, its relatively low mechanical strength requires more insulating pads and bindings for fixation, which will occupy a certain amount of internal space. Moreover, its appearance is not neat, and its overall size is slightly larger than that of the cast transformer with the same capacity.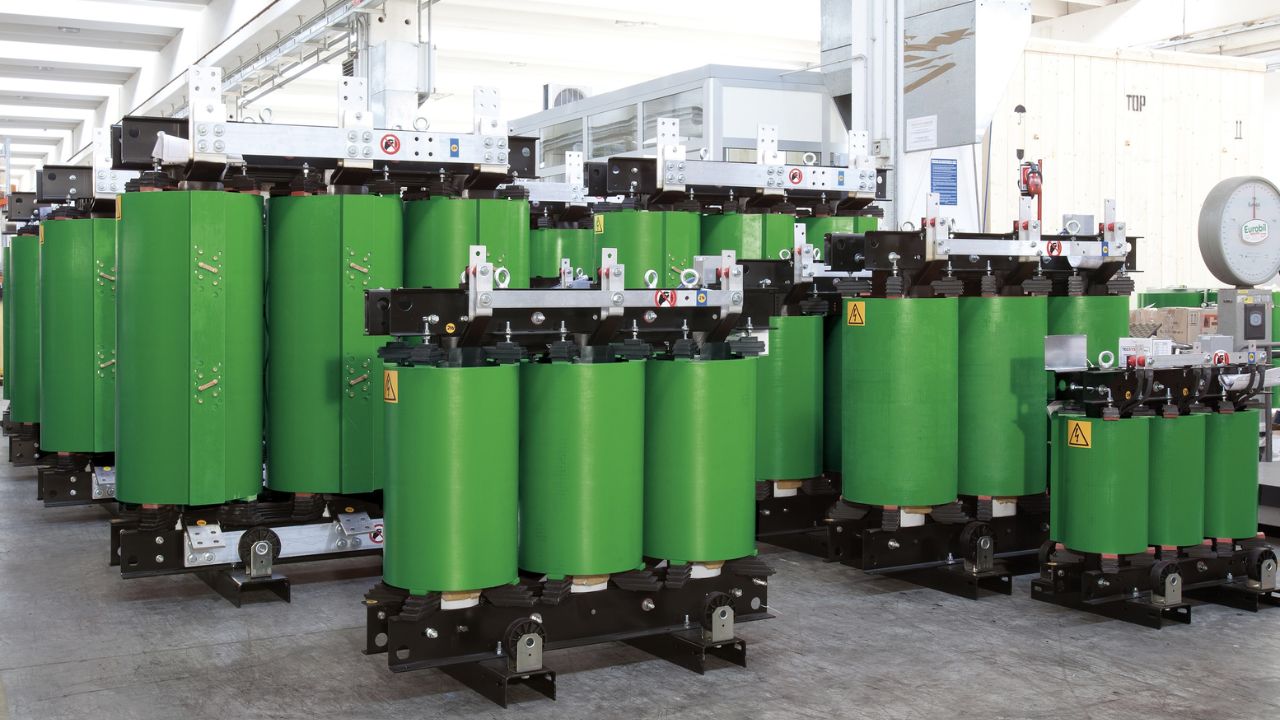
Insulation Class
The insulation class can also be regarded as the heat resistance class, which indicates the long-term operating temperature that the insulating material can withstand. For example, class H can reach 180℃, class F can reach 155℃, and class B allows up to 130℃.
If you choose a higher insulation class, it also means allowing for a higher temperature rise. When designing an H-class transformer, it is designed to tolerate higher operating temperatures, thus being able to handle a greater current, or it can reduce the heat dissipation area while keeping the same capacity.
Therefore, adopting a high insulation grade is one of the key technologies for achieving small and compact transformers. It enables the transformers to operate at higher temperatures and allows for the use of less material or a more compact structure to meet your capacity requirements.
Winding Construction
The winding construction directly determines the space utilization rate and electromagnetic performance, and is the core of power conversion. The winding structure mainly consists of winding type and winding arrangement method.
The foil winding can achieve a higher space utilization rate, which is beneficial for achieving a larger heat dissipation area with a lower thermal resistance. The wire winding is mainly wound with insulated wires and is suitable for various voltages and capacities, with high flexibility in use. However, the gaps between the wires result in a lower space utilization rate. Compared with other methods, the transformer size of the wire winding with the same current is larger.
For different winding arrangements, they can be roughly classified into concentric winding and interleaved winding. The former has a simpler structure and the high-voltage winding has a longer heat dissipation path. The latter can effectively reduce short-circuit impedance and leakage flux, but its structure is more complex and the insulation treatment is more troublesome. You may not choose the latter simply because of reducing size while considering electrical performance.
Apart from the above factors, the core material, rated voltage and insulation level, and the protective enclosure, also affect the size of the dry type transformer. As above mentioned, higher voltage levels are the fundamental factor causing the increase in size. Besides, if you also want to achieve a higher Propriété intellectuelle protection level, a higher-rated enclosure will significantly increase the volume and weight.
How to Measure Dry Type Transformer Sizes
Measuring the dimensions of dry type transformers is a precise match among your electrical requirements, assessing physical space and installation feasibility.
KVA Requirements and Other Electrical Parameters
Determining the KVA requirements and electrical parameters is the most crucial step.
Calculating the KVA demand requires considering diversity and development, and ultimately determining a safe, economical, and continuous power supply capacity. You need to calculate all your load equipment and figure out the voltage and current at which they operate. All the loads are uniformly calculated using KVA. The basic formula is KVA = kW / PF (Power Factor).
You must be clear that not all the equipment will operate at full capacity simultaneously. The demand factor indicates the actual usage intensity of some equipment, and the coefficient also reflects that the peak periods of different types of loads do not completely overlap. These two factors can help you better calculate your actual load power.
Apart from the total load power for practical application, you also need to add a common margin, usually ranging from 15% to 25%. This can provide space for future expansion and prevent frequent transformer replacements due to increased load.
Therefore, based on the standardized rated capacity levels of the transformer, you should choose the minimum standard capacity that is greater than the final demand. If the calculated value is very close to a certain standard capacity, you should fully consider your load type, or choose a higher-level standard capacity for safety reasons.
Physical Dimensions
After clarifying your actual electrical requirements, you need to consider the actual physical dimensions of the transformer, including its length, width and height.
You also need to consider the dimensions of the external interfaces and protruding parts of the transformer. Additionally, the weight of the dry-type transformer needs to be measured. The weight includes the total weight and the center of gravity. This is related to the transportation equipment and methods for the transformer.
Besides, the cooling and maintenance channels of the transformer, the protection level, and the safety of the wall-mounted installation must all be clearly planned before the installation. The investigation of transportation and installation routes also needs to be completed before the transformer is ordered and installed.
Size Considerations for Selection and Installation
Type d'application
The first step in choosing a dry-type transformer is to determine the type of application for the transformer. The application type serves as the starting point for size considerations, and it determines the priority of the transformer design.
If you apply dry-type transformers in industrial or manufacturing industries, you should fully consider the IP Class of the transformer, its ability to withstand shock and vibration, and also leave sufficient maintenance space for regular inspections and cleaning. If the environment is highly dusty or humid, you should choose an IP23 or higher. Using a protective enclosure will also increase the size of the dry-type transformer.
In commercial building applications, you should consider the requirements for safety, fire prevention, low noise and aesthetics. In IT rooms, you should choose dry-type transformers with ultra-high power density, compact design and high reliability.
Transformer Specifications
Check the specifications of the transformer, including voltage level, KVA rated value and capacity margin, etc. The voltage level directly affects the size of the windings, insulation thickness and more settings. But the large size resulting from the voltage level cannot be solved by design optimization.
KVA capacity is the main driving force for determining the size. When purchasing, it is necessary to fully consider the relationship between future expansion and current occupied space. After all, margin also means larger size and higher cost.
Besides, you also need to consider whether special customized harmonic load conditions are required.
Installation Environment
Besides the humidity, dust, temperature and other factors mentioned above for specific locations, it is equally important to investigate the on-site installation environment. This is also the aspect that is most easily overlooked.
You need to check whether the transportation route allows the transformer to pass through smoothly. Does the final installation space meet the local installation standards? Are the ventilation conditions satisfied? For large transformers, does the load-bearing condition of the installation location meet the requirements? Every detail of transportation and installation needs to be carefully considered during the selection process.
FAQ
How does Voltage Rating Affect Dimensions?
Simply put, the higher the voltage level, the larger the size of the transformer. As the voltage level increases, the insulation requirements also increase sharply. Therefore, the windings also need to become thicker and larger. More advanced insulation structures and materials will also occupy more space. The heat dissipation design also needs to be comprehensively considered.
Does Low Temperature Rise Design Require a Larger Heat Dissipation Area or More Materials?
Yes. The core objective of the low temperature rise design is to keep the operating temperature of the transformer at a relatively low level. This is mainly achieved by increasing the heat dissipation area and using more or better materials. Low temperature rise has lower losses and higher reliability. It is the preferred choice for high-end manufacturing, data centers.
How does Insulation Design Impact Volume?
The heat insulation design will increase the volume of the transformer. The heat insulation effect achieved by thickening the casing and adding heat insulation materials will occupy more space, resulting in an increase in the external dimensions of the transformer and thus an increase in its volume.
What does a Dry Type Transformer Specification Include?
The specifications of dry type transformers include electrical parameters(rated capacity, voltage combination, impedance voltage), structural features(cooling method, insulation class, IP rating), performance indicators(load loss, temperature rise limits), physical and environmental parameters(installation method, dimensions, weight).
Final Thought
KDM is a professional manufacturer of custom electrical enclosures. We can produce dry type transformers to meet your different electrical needs. We strictly control the raw materials to provide you with high-quality customized products.We will respond to your customization requirements within 1 to 3 days and provide you with a comprehensive customized solution. If you have any customization needs related to electrical enclosure, please feel free to Contactez-nous.



