PDU is responsible for distributing power to IT equipment within cabinets in a data center. The correct PDU can achieve safe, reliable and efficient power transmission and support operational functions. This article provides you with a detailed guide for selecting the correct PDU. Hope this article can help you choose the appropriate PDU for your data center or IT infrastructure.
What Is a Power Distribution Unit?
The power distribution unit (PDU) is mainly installed in racks or cabinets (IT enclosures). The PDU is used in data centers to safely and reliably distribute the power from the upstream source (UPS or facility power supply) to servers, network devices, and other IT equipment.
Modern PDUs also have features such as remote monitoring, overload prevention, and support for redundant power supply, which improve the operational time and efficiency of the equipment.
The PDU is fundamentally different from the household power strip. PDU has a higher current capacity and a greater outlet density. The PDU typically uses industrial connectors in accordance with the IEC standard. The PDU also integrates functions such as circuit protection, power monitoring, and remote control, and is an important component of the manageable infrastructure in data centers.
Types of PDUs and Its Application
PDU can be classified according to the installation method as vertical PDU or horizontal PDU. It can also be categorized based on the energy characteristics of the input or output. The following mainly introduces the classification based on functions and intelligence levels.
Basic PDUs
The basic PDU is the simplest form of power distribution unit. It only provides power distribution and basic overload protection. It does not have any monitoring or management functions. Its price is the lowest and its structure is simple.
The basic PDU is mainly applied in non-critical and low-density load scenarios, such as test environments, non-core network devices, and IT equipment in office areas. In scenarios with limited budget and no need for remote monitoring, you can also choose the basic PDU.
Metered PDUs
The metered PDU adds the power metering function to the корпус. It features a digital display that allows you to directly view the total current, voltage, power and load level of the PDU. This can provide energy consumption data, helping to support better capacity planning and preventing overloading of the cabinet.
Функции:
Capacity Planning: Helps you monitor the load trend of the cabinet and prevent overloading.
Calculate the Base Cost: Helps you roughly calculate the energy consumption for different cabinets used.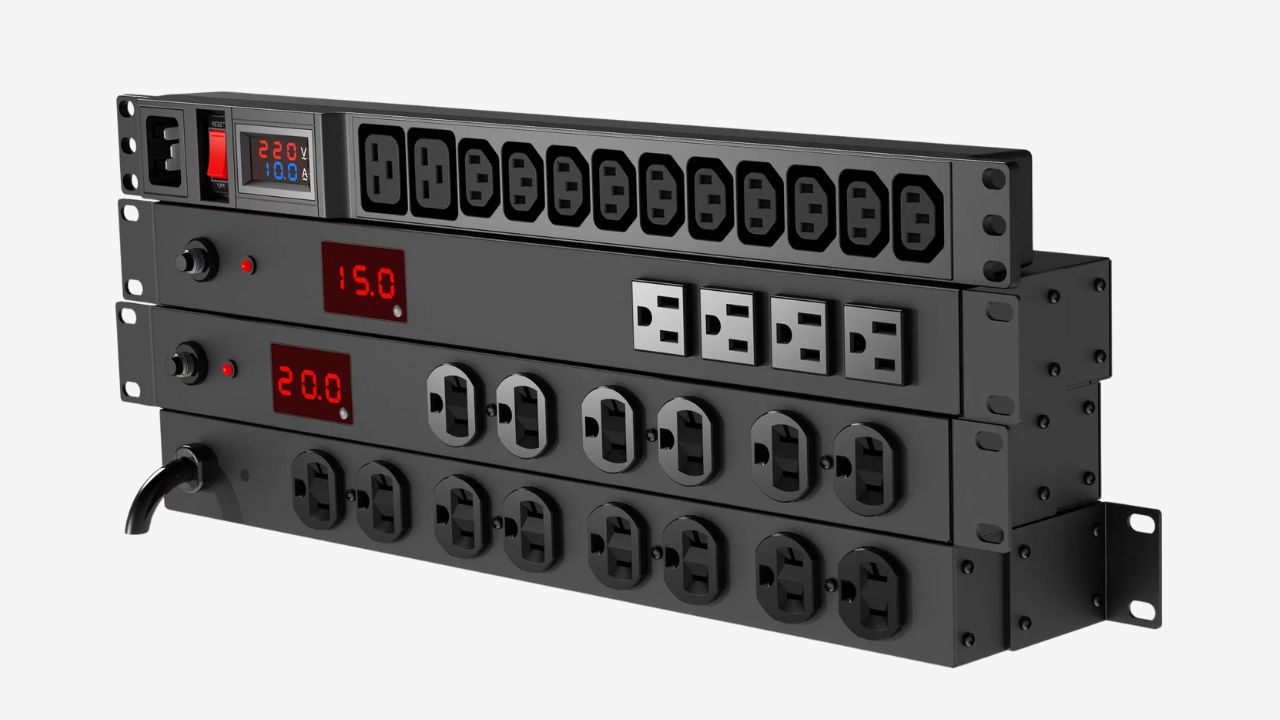
Monitored PDUs
The monitoring PDU adds network connectivity(SNMP, web interface), and its digital metering display enables you to conduct local and remote monitoring. You can monitor and record real-time and historical power data at the rack or outlet-level through the network interface or the network management system.This can help you to optimize power consumption.
It also supports setting limits for parameters such as current, and will send an alert if the limit is exceeded. You can apply it to data centers that require remote energy consumption management, which can help you improve efficiency and reliability.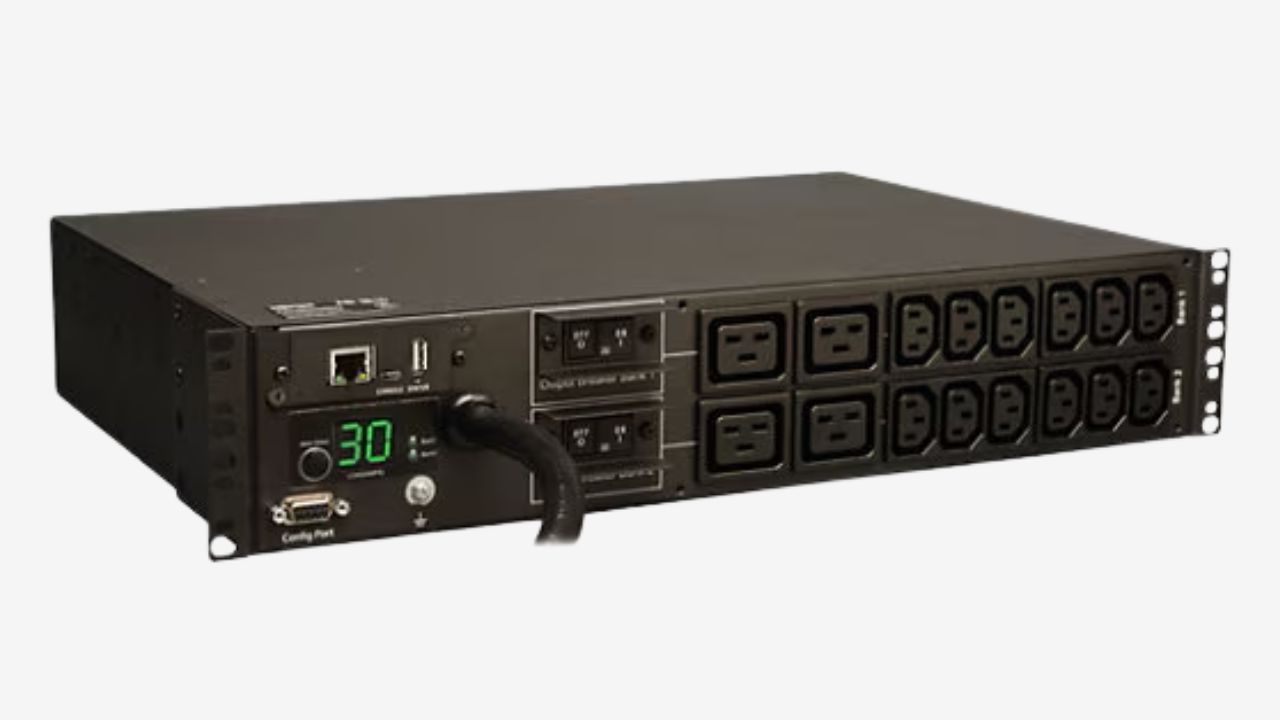
Switched PDUs
The switched PDU combines monitoring and remote outlet control. It allows you to remotely turn on or off individual outlets without physical contact, allowing for the power cycling of the device.
Its main features are remote monitoring and outlet level switching, which enables faster fault detection and recovery, significantly improving operational efficiency and reducing the cost.
You can use the switched PDU in dynamic data centers where remote access and flexibility are required.
Intelligent PDUs
The intelligent PDU is the most powerful type of PDU. It provides comprehensive monitoring, control, and data analysis. It integrates with DCIM or BMS, and can also be equipped with environmental sensors for temperature and humidity.
Its main functions include advanced power and environmental monitoring, outlevel-level control and measurement, the data center management integration, and improvement of energy efficiency and capacity planning.
Intelligent PDUs are most suitable for modern, high-density and remotely managed IT enclosures. The control and scalability of the enclosures are of vital importance.
How to Choose the Right PDU for Your Data Center
Identify Your Power Requirements
Clarifying your power requirements is the foundation of all decisions. First, you should list all the existing equipment inside the enclosure and record the key parameters of each device, such as the number of power supplies, rated power, and connector type. Then, you need to calculate the current total load and peak load.
Besides considering the current load, you also need to leave margin for future expansion. Usually, you need to plan for capacity expansion in the next 1 to 3 years, and think whether it is possible to install higher density servers. Generally speaking, the margin is usually higher than the maximum load current estimate of 20% to 30%.
Beyond the analysis and planning of current and future loads, you also need to confirm the power type for the cabinet’s power supply. Is the power supply equipment single-phase (120V/230V) or three-phase (208V/400V)? Guarantee that the input voltage of the PDU matches with it, which can guarantee electrical compatibility and system safety. Incorrect connections will directly burn out the PDU and the downstream equipment.
It is necessary to make sure the type of connector and the rated current. This is mainly to provide a basis for the design of redundant architectures. For high-availability enclosures, you also need to deploy two-way PDU units A and B.
Choose the Right Type of PDU
Based on your monitoring management requirements, you can combine the above-mentioned PDUs and their applications to determine the functional hierarchy of the PDU.
Basic PDU: Only supplies power. Suitable for stable, low-density loads. Lowest cost.
Metered PDUs: Provide total energy consumption data at cabinet or circuit level. Used for capacity planning and to prevent circuit overload.
Monitored PDUs: Provide remote power monitoring, network connectivity, and support alerts and reporting.
Switched PDUs: Provide remote monitoring and outlet-level switching. Allow faster fault diagnosis and recovery, and can elevate the efficiency of operation.
Smart PDUs: Advanced power and environmental monitoring.Outlet-level control and metering.Integration with data center management platforms.
Consider Form Factor and Mounting Options
The main objective of this stage is to guarantee that the PDU is physically compatible with your cabinet. The mounting methods you can choose include vertical PDU and horizontal PDU.
Vertical PDUs: The vertical PDU is mainly installed in the zero-U space on both sides of the cabinet. It does not occupy the installation space of the equipment and supports high-density deployment as well as clear A/B power path isolation. When installing the vertical PDU, you need to precisely measure the available depth of the cabinet to make sure that the length of the PDU is appropriate.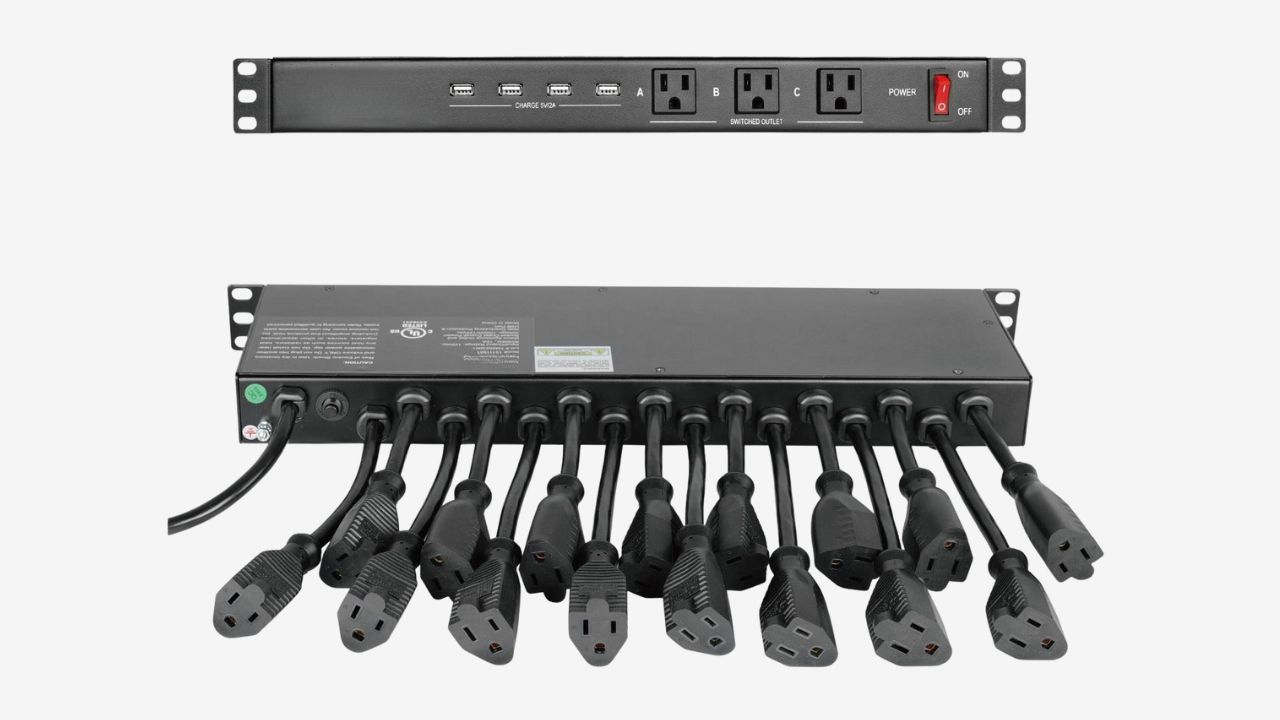
Horizontal PDUs: The horizontal PDU needs to be installed on a 19-inch rack rail like a server. This allows you to deploy flexibly. Before installation, you need to guarantee the available U-space, usually ranging from 1U to 2U. Additionally, you must verify that the depth of the PDU matches the cabinet.
Outlet Configuration and Compatibility
The configuration of the outlets works as the direct interface for connecting devices and requests precise matching. First of all, you need to increase the total number of outlets required by the equipment by 20% to 30% as a reserve, to accommodate future additions of equipment and temporary needs.
Secondly, you also need to reckon the type of the outlet. The common types of outlets include C13 (suitable for most servers and network devices, with a rated capacity usually being 10A/16A), C19 (used for higher-power devices such as high-end servers, UPS, etc., with a rated capacity usually above 16A) or American standard.Of course, you can also consider choosing a hybrid configuration PDU to flexibly support different types of devices.
Finally, you need to select the appropriate outlet arrangement and gap. Proper spacing and layout facilitate the insertion and removal of large power plugs and are also beneficial for cable management.
Redundancy and Reliability Requirements
During this stage, the main focal point is on establishing resilient power paths for critical business operations. This primarily indicated in the following three aspects:
Device-Level Redundancy: For dual-power devices, you must provide two independent power paths for each of the two power supplies. This requires two PDU units, and they should be connected to different upstream UPS or distribution cabinets respectively.
PDU-Level Redundancy: The two PDUs mentioned above form two redundant paths. They use the same configuration to guarantee load balance and operational consistency.
Internal Component Redundancy: For extremely high availability scenarios, you can consider equipping a high-end smart PDU with dual power modules and dual management modules for data centers. This can effectively prevent the PDU from becoming a single point of failure.
Monitoring, Management, and Networking Features
Monitoring Level: Determine whether you need cabinet-level or outlet-level data. The former is of the metering type, while the latter is of the intelligent type.
Network Connection: You need to confirm the network interface and the required management VLAN or IP address. Moreover, you must check the supported protocols to guarantee that it can be seamlessly integrated with your DCIM/NMS system.
Remote Control: The remote start function is the core. It can help you assess the usability of the control interface, the security of Role-Based Access Control(RBAC), and the integrity of the operation logs.
Alerting Capabilities: You need to guarantee whether the PDU supports sending alerts such as Email, SNMP Trap,and whether it can detect and report power-off events on the device side.
Energy Efficiency and Power Management
If you want to use PDU to optimize your data operation costs and sustainability, you need to choose an intelligent PDU to assist you in measurement and optimization. The intelligent PDU can help you achieve the following:
Precise Measurement: The data provided by the intelligent PDU can help you eliminate inefficient servers and optimize load distribution.
Capacity Optimization: The real-time monitoring of the intelligent PDU enables you to deploy new equipment in the racks to maximize the utilization rate of the existing infrastructure.
Environmental Linkage: It can be combined with temperature and humidity sensors to implement more precise cooling strategies.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
To make sure that your investment can adapt to future developments, you need to select a PDU with a higher rated power than the current requirement, to reserve space for future equipment with higher power density.
You can also choose high-end PDUs with modular designs to facilitate future functional upgrades. Besides, you need to consider whether the PDU supports new communication and management standards, so as to integrate into future automated operation and maintenance.
Compliance, Safety, and Standards
Guarantee that products comply with regulatory requirements, this is the key to protect the safety of personnel and equipment. PDUs need to undergo mandatory safety certifications in the deployment areas, such as УЛ (North America), CE (Europe), etc. The performance and quality of PDUs should meet the relevant IEC or ISO standards.
The installation of the PDU should also comply with the electrical installation standards of the country or region. Moreover, the PDU should be equipped with devices such as автоматические выключатели that offer protection against overcurrent, overvoltage and power surges.
Budget and Total Cost of Ownership(TCO)
Besides the costs related to the PDU hardware, installation kits or modules, you also need to comprehensively consider the operational costs, risk costs, etc. Operational costs include the electricity savings achieved by the intelligent DPU through load optimization and the elimination of redundant equipment. Also, there are the savings in labor costs and time costs.
Ultimately, you need to conduct a TCO assessment for all factors. Calculate the initial investment cost of the PDU, as well as the long-term value brought by the reduced operation and maintenance costs and extended infrastructure lifespan of the PDU in the data center. From this perspective, the TCO of the intelligent PDU is superior to the basic PDU in data centers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a PDU
Incorrect Outlet Type
E.g. C13 outlet is configured for high power devices that should use C19, try to solve with a converter.
Using mismatched rated outlets can cause them to overheat, melt or even start fires. You should guarantee that the PDU has a sufficient number of C19 or other high-power outlets of the corresponding specifications.
Ignoring the Management
E.g. The smart PDU is applied without planning the network connection, integrating into the DCIM system, and specifying the corresponding monitoring and alerting processes.
The intelligent functions fail to demonstrate their value, resulting in waste of funds and a significant reduction in the investment return rate. By applying intelligent PDU and treating it as a part of the IT assets, you should plan the network architecture, management software and operation and maintenance processes in advance.
Mixed PDU Brands and Standards
E.g. During different periods and for different projects, multiple brands, various models of PDUs were purchased, and the components were not interchangeable.
This will undoubtedly increase the difficulty of operation and maintenance, and you will also need to learn multiple systems. This will also greatly reduce the efficiency of troubleshooting. Therefore, you should standardize the PDU product line in the data center and conduct unified management and maintenance.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Do You Need Per-Outlet Power Monitoring to Locate Zombie Servers or Achieve Accurate Load Balancing?
Yes. Only the monitoring of outlet-level can provide independent power consumption data for each server. This enables the identification of zombie servers and allows for precise load distribution and adjustment based on the actual working status of each device. The total power consumption data of the cabinet cannot achieve the above goals.
What Details Should be Considered Regarding the Network Management of the PDU Besides the Basic IP Access?
Besides basic IP access, PDU network management must also consider security protocols, access control, integration capabilities, alert mechanisms, network design, availability, and bulk management.
What Should be Noted When Choosing a PDU in a 208V Three-Phase Environment in North America?
You should think about input compatibility,ensuring the PDU input matches a 208V three-phase power source and the plug type is fully compatible. You should select a PDU that allows it to evenly distribute the output outlets across all three phases.
Intelligent PDU is preferred, which is the key to realize effective load balancing and prevent overload. Besides, you need to pay attention to the compatibility of outlet types, redundancy design, and whether the depth and load-bearing capacity of the three-phase PDUs support the cabinet.
Final Thought
KDM is a professional manufacturer of custom electrical enclosures. With many years of experience in custom production and partnerships with several renowned brands, we can provide you with a variety of electrical enclosures for your data center or IT infrastructure construction, including enclosures of various materials, features, and installation methods. You can provide us with your custom design, and we will respond promptly and offer you a delicated custom solution. Please feel free to связаться с нами.



