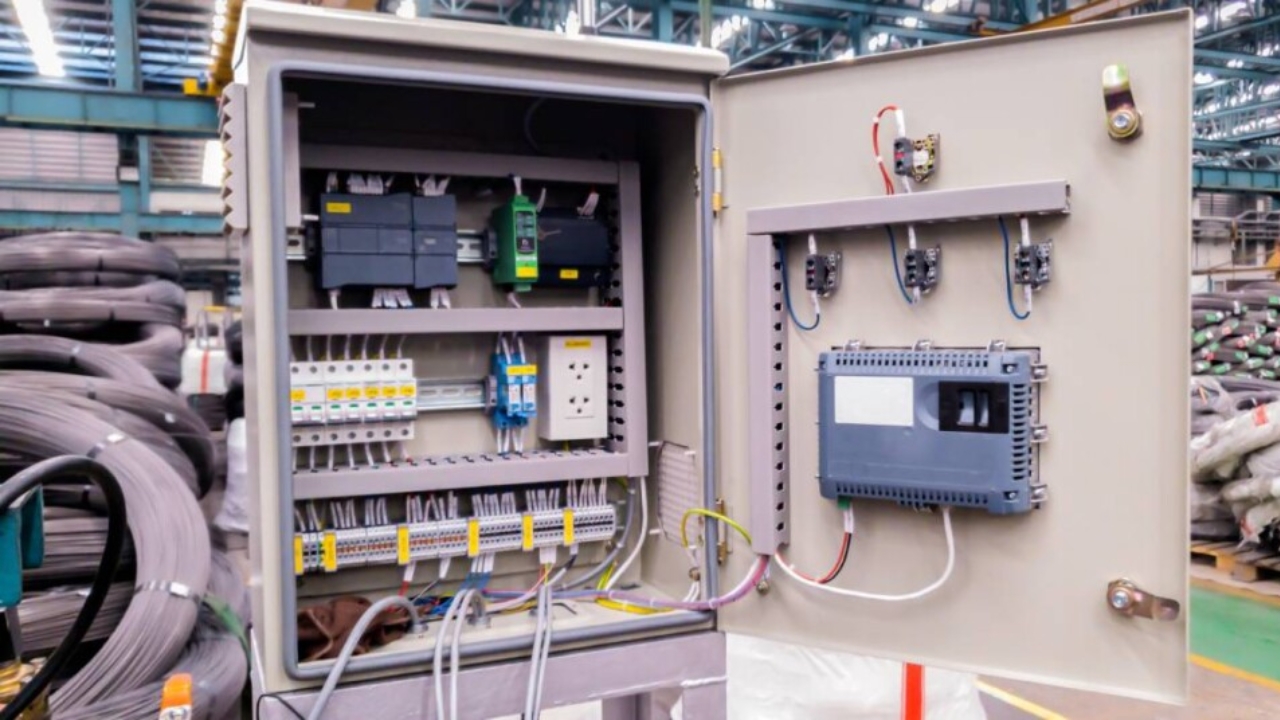
Basically, an electrical enclosure may come either as metallic or non-metallic. And, as you know, using the right electrical enclosure suited for your purpose is critical to the performance, safety, and durability of your electrical systems.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key differences between both types of enclosures and their best use cases.
What Are Electrical Enclosures?
Электрические шкафы are electro-protective housings that look a lot like a box. Although box-like, these kinds of enclosures are built and designed to house electrical or electronic components. Hence, they are also known as electrical cabinets.
Electrical enclosures first protect you from likely electric shocks associated with electricity. Aside from protecting you, they shield internal parts (the electric components within) from dust, moisture, chemicals, physical impact, and access by random persons.
Electrical enclosures are either metallic or non metallic. Because of these differences in materials, the different electrical enclosures available, regardless of how similar they look, have different strengths, corrosion resistance, thermal tolerance, and design flexibility levels.
Properties of Metallic and Non-Metallic Electrical Enclosures

What Are Metallic Enclosures?
Metallic enclosures, like its name, are made from conductive metals like steel or aluminum. On some occasions, copper alloys can be used to make metallic enclosures. Metallic enclosures are rigid, so they are great choices for high-impact environments.
Common Materials Used to Make Metallic Enclosures
Some of the most common electrical enclosure materials включать:
- Steel: Steel is strong and cost-effective. Its strength makes it a befitting material for making electrical enclosures often used indoors.
This steel is also available in different forms depending on the materials added to the basic steel. There’s the normal steel, Корпуса из оцинкованной стали (galvanneal or carbon steel), and CRCA (cold rolled close annealed steel). These are strong, durable, and malleable, so they are fit for heavy-duty electrical enclosures. Steel is prone to rusting, so it’s best used in non-corrosive situations.
- Stainless Steel: Usually, Корпуса из нержавеющей стали are rust-resistant and durable. This makes them the ideal choice for industrial purposes or hygienic environments.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, inexpensive and fairly corrosion-resistant. As a result, it’s a great choice for both indoor,industrial, and outdoor use.
- Copper: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, so it’s good for making electrical cabinets. Copper, however, can be expensive, so it’s not often used.
Strengths of Metallic Enclosures
Strengths of metallic enclosures include:
- Metallic enclosures are built to withstand physical stress, high temperatures, and mechanical impacts, so they are durable.
- Because metals are conductive in nature, grounding metals is usually a straightforward process. This metallic nature also shields sensitive electronics from electromagnetic interference.
- Metals offer better fire protection compared to non-metals.
- Metals are easier to restructure into different shapes and sizes.
Applications of Metallic Enclosures
- Industrial plants and factories
- Generator or power distribution units
- Machine control panels
- High energy areas
What Are Non-Metallic Enclosures?
Non-metallic enclosures are electrical cabinets or enclosures that are constructed from non-metallic and usually man-made raw materials like polycarbonate, fiberglass, or ABS plastics.
Often, non-metallic electrical enclosures do not conduct any form of electricity. In addition, they are lightweight and resistant to corrosion when compared to all metals. This ability to resist corrosion makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Common Materials Used to Make Non-metallic Electrical Enclosures
Они включают в себя:
- Polycarbonate: Has a high UV-resistance, strength and impact-resistance. Hence, it’s great for outdoor settings.
- Fiberglass: Extremely durable, a good conductor of electricity, and it’s corrosion-proof too.
- ABS Plastic: ABS plastic is lightweight and budget-friendly. It’s ideal for general-purpose or simple indoor use.
- Polyester: Solid and fairly durable, but it has superior resistance to corrosion substances. However, it can get quite brittle during weather.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Polyester (FRP): Since it’s a mix of two non metallic materials used for making electrical enclosures, it combines the strength of both. This makes FRP more durable than other non metallic materials for electrical cabinets.
Strengths of Non Metallic Enclosures
Generally, non metallic materials used to make electric enclosures and cabinets are:
- Resistant to corrosion
- Легкий
- Excellent insulators, and they enhance safety by preventing accidental shocks
- Are flexible and easy to design. They are available in various colors, shapes, and custom moldings.
Applications of Non Metallic Electrical Enclosures

- Telecommunications and IT boxes
- Home distribution boxes
- Water treatment and chemical facilities
- Coastal and marine environments
- Outdoor signage and kiosks
Key Differences Between Metallic and Non-Metallic Enclosures

There are several differences between the metallic and non metallic enclosures aside from the nature of materials used to make them. These differences include:
1. Durability & Impact Resistance
Metallic electrical enclosures have a higher mechanical strength, so they can handle physical abuse in environments where heavy-duty machines are used.
This ability to resist impact is not very possible with most non-metallic electrical enclosures or cabinets. Nevertheless, certain high-grade polycarbonate, FRPs, and fiberglass enclosures may have a relatively higher impact resistance compared to other non metals.
2. Corrosion Resistance
The ability of a material to be corrosion resistant is a factor of how the materials react to moisture and chemicals. Metal enclosures (unless those made of stainless steel, copper, or treated) are prone to rust. Non-metallic enclosures, on the other hand, are more resistant to corrosion, so they are better fit for wet or industrial environments with corrosive chemicals.
3. Portability
Metal enclosures, because they are made with metals, are heavier, so you will need more effort to carry them and also to install them. This can be tiring when one wants to install large panels. Non-metallic enclosures have a lighter weight, and installing them is easier (or installation appears easy), so they are better for remote or elevated areas.
4. Electrical Conductivity and Grounding
Since metallic enclosures can conduct electricity, they must be properly grounded too as grounding is vital for EMI shielding. Non-metallic enclosures do not conduct electricity, so there’s no need for grounding and reducing the risk of accidental shocks.
5. Flexibility
While metallic enclosures are malleable and have a rigid industrial appearance, non-metallic electrical enclosures have a more flexible shape. The flexibility also makes customization of the cabinets easier. So where the customers are particular about designs of the enclosures, non metallic options will do.
6. Initial and Long-Term Costs
Metallic enclosures are on the expensive side. Where you have to pay on installments, metallic enclosures have higher upfront costs. However, they are more durable over time, so may incur less costs. On the other hand, non-metallic enclosures, which are often cheaper at first, may degrade under constant sun or extreme temperatures unless they are UV-stabilized.
When to Choose Metallic or Non-Metallic Enclosures

Choose Metallic Enclosures if:
- You need maximum mechanical protection in harsh or high-risk industrial settings
- Your electrical components in the enclosure need EMI shielding or strong grounding
- The temperature of the environment fluctuates often, and it’s prone to fire risk
- You can afford the costs
Choose Non-Metallic Enclosures if:
- You’re working in a wet, salty, or chemical-rich environment
- The setup needs to be lightweight and easy to handle
- Electrical insulation and safety are top priorities
- You want design flexibility or are installing in a visible, public-facing area
Final Verdict: Which Is Right for You?

Knowing what to choose between metallic and non-metallic electrical enclosures balls down to how you want to use them.
If you’re still unsure at this point, consider making your firm a hybrid environment where a mix of both enclosure systems can be used.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Are metal enclosures better than plastic?
It depends on the use case. For instance, metal enclosures are better when strength is needed but not for wet or corrosive areas. Non-metallic enclosures are safer and are more insulating.
Do non-metallic enclosures need grounding?
No. Non metallic enclosures don’t need to be grounded because they don’t conduct electricity.
Which enclosure is best for outdoor use?
Usually, non metallic electrical enclosures like fiberglass or UV-stabilized polycarbonate enclosures are better for outdoor use because they are light and cheap. Stainless steel and aluminum also perform well outdoors but are heavier and more expensive.



