Globalization, smart grids and industrial automation are driving a rapidly growing demand for standardization of electrical enclosures. This article discusses the importance of electrical enclosures, specific standards and technical requirements. Whether you are electrical engineers or system integrators, this article can provide you with a clearer understanding of standardization.
Definition of Electricity Enclosures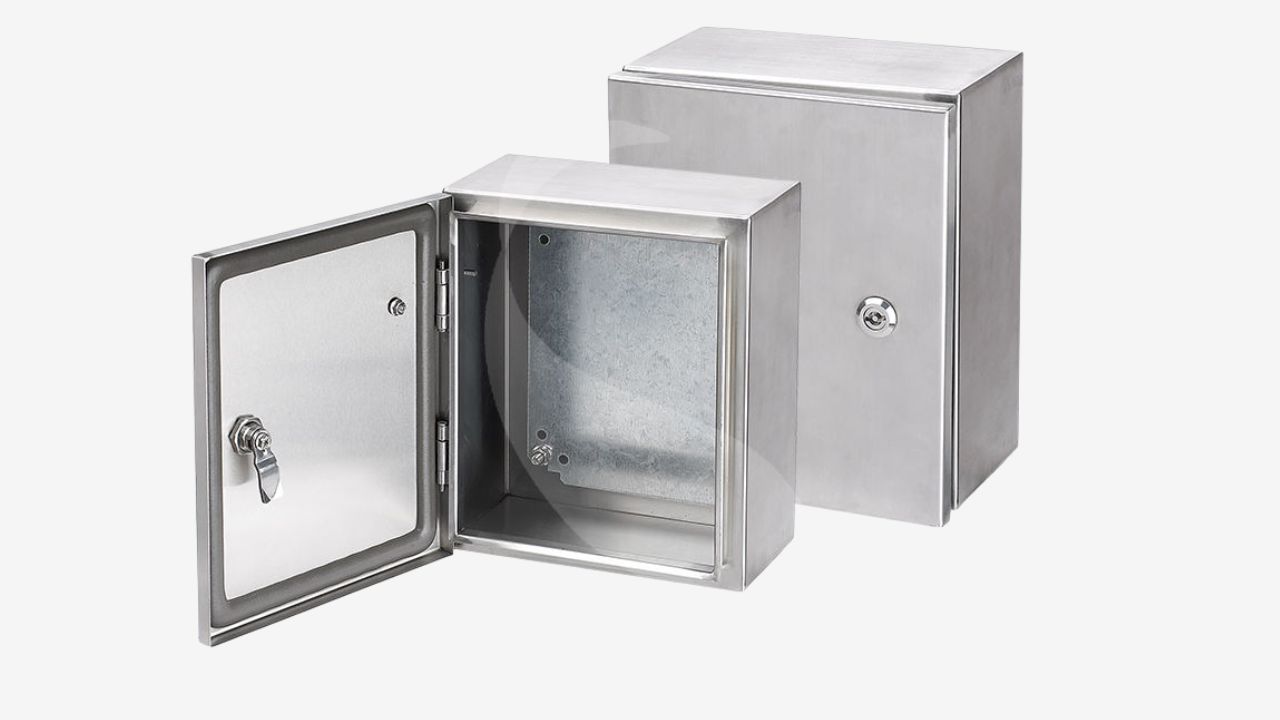
العلب الكهربائية are also known as chassis, control cabinet or distribution boxes. It is a physical housing specifically designed to contain and protect electrical, electronic or automated equipment. Its core value lies in providing a safe, reliable and durable operating space for internal sensitive components in the intended application, while ensuring the safety of operators.
عناصر: A well-functioning standardized electrical cabinet typically consists of multiple parts, including the enclosure body, door panel, mounting rail, backplate, and cooling system. Each component is designed according to standardized considerations. Each part has an important function.
Common Material: The electrical enclosure is usually made of cold-rolled steel (CRS), الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, الألومنيوم, engineering plastic or fiberglass. The choice of materials directly determines the cost, protective capacity, lifespan and applicable environment of the enclosure.
طلب: Electrical enclosures can be applied in almost all fields of power consumption and control, including industrial automation and control systems (PLC control cabinets, frequency converters), energy and distribution (low/medium voltage switch cabinets, outdoor distribution boxes), commercial and special fields (data center cabinets, medical equipment enclosures, explosion-proof enclosures), etc.
Importance of Standardization
Standardization of electrical enclosures is the backbone of a modern industrial infrastructure that is safe, efficient and interconnected. It unlocks productivity and innovation potential by setting minimum requirements.
اعتبارات السلامة
The most crucial and core task of standardization is to guarantee the safety of personnel and equipment.Standardized specifications translate safety principles into concrete specifications that can be implemented and tested.
To guarantee personal safety, the electrical enclosure has clear protection grades, including IP standards (dust and water resistance) and IK standards (impact resistance). Besides, the electrical enclosure also has a unified grounding standard to prevent electric shock. It has clear requirements for the safety properties of materials (flame retardant grade, insulation strength), which can prevent internal faults split and the fire spread.
To guarantee the safety of equipment and operation processes, the standard also provides environmental adaptability and thermal management specifications for electrical enclosures. It can specify material, coating and sealing requirements according to different environments and provide guidance for ventilation and heat dissipation design.
By establishing quantifiable safety thresholds, the standard specifies specific standards for products, such as UL 508A and IEC 61439. You only need to confirm that the product meets the standards to trust its basic security.
Interoperability and Compatibility
Interoperability and compatibility can directly elevate the efficiency and flexibility of the drive system and are also the most direct economic benefits of standardization. It usually includes physical interoperability and system compatibility.
Physical Interoperability:
- The unification of size and structure. You can seamlessly install circuit breakers and PLCS from different manufacturers in the same cabinet. This simplifies design, installation and later renovation.
- The cable interfaces are unified, and the accessories and peripheral devices can be used interchangeably.
System Compatibility:
- If you use a standard enclosure layout, you can simplify engineering, shorten design cycles, and reduce errors.
- You can also quickly switch to a different brand of enclosure in case of failure, which improves the flexibility of your application.
- The standard enclosure can also promote modular construction and provide basic units for prefabricated substations.
Quality, Reliability, and Lifecycle Management
Consistency: The standards stipulate process parameters such as the material thickness, coating quality, welding strength, and coating adhesion of electrical enclosures, ensuring stable performance across different batches of your products and preventing quality decline.
Test: The standard also conducts verification tests on temperature rise, short-circuit withstand strength and more to guarantee that your enclosure has undergone strict verification during the design stage.
Predictable Lifespan: Based on tests conducted with standard materials and under standard conditions, you can more accurately predict the service life of the enclosure.
Simpler Maintenance and Upgrade: Components standardization makes it easier to purchase and replacement parts. Even if the equipment is upgraded, new components can be easily installed within the original standard framework.
Regulatory and Market Benefits
National security regulations often directly quote or are based on international standards(IEC). This is also the most direct way to prove that the enclosure meets the standards.
Obtaining international standard certification(UL, CE) is a mandatory requirement for enclosure to enter the global market. Standardization can greatly simplify the cross-border certification process.
Manufacturers for standard series can carry out large-scale production, reducing production cost.
You can also simplify the purchasing process, which is better for price comparison and competition.
Producers following the same technical rules can create a fair competitive environment and innovate about quality, service and high added value.
Standardization resolves fundamental security and compatibility issues, which is conducive to R&D focusing on cutting-edge innovations such as intelligence and energy efficiency improvement.
International and Regional Standards
IEC Standard for Electrical Enclosure(International Standard)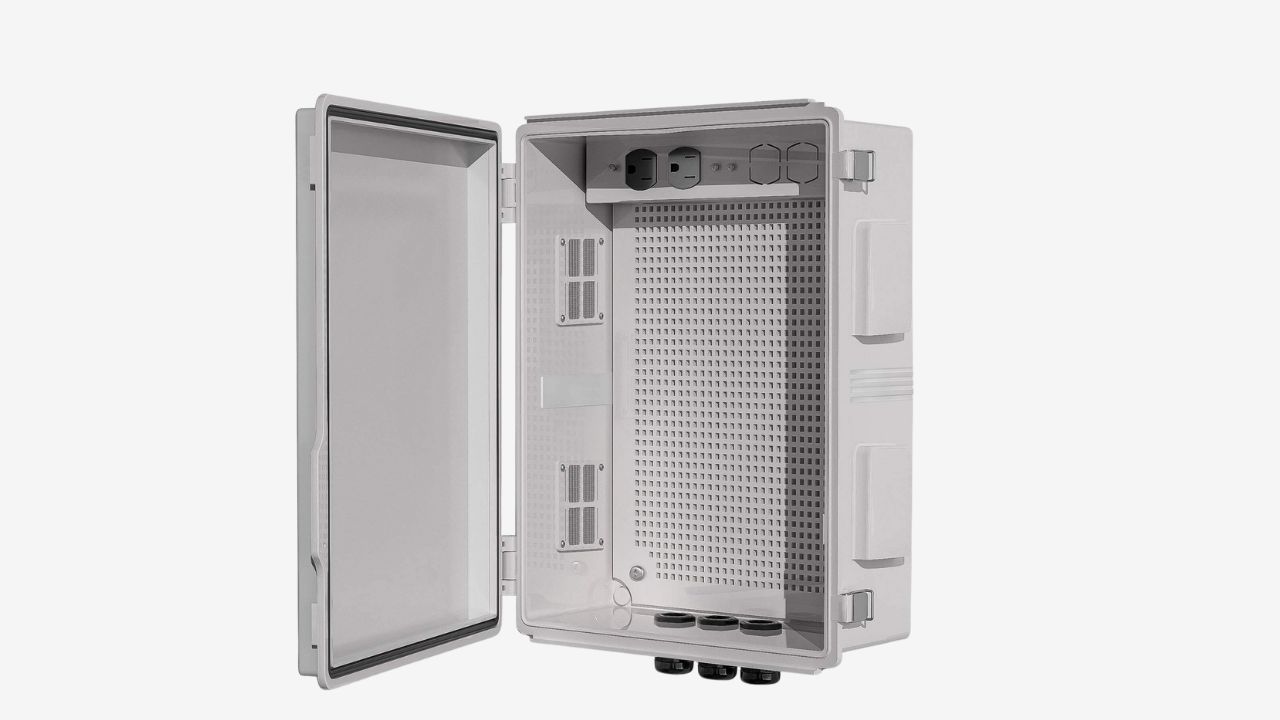
IEC 60529(تصنيف IP)
It is a globally (except for North America) universal classification system for protection levels. The IEC standard mainly defines test methods, which convert protective performance quantities into IP codes. It mainly focuses on the protection against solid objects(0-6 rating) and water(0-8 rating).
It allows manufacturers and you to clearly communicate the environmental protection level. However, IEC does not address safety requirements such as structure and corrosion resistance. It is not a product certification standard either.
IEC 62208(For Empty Electrical Enclosures)
This IEC standard is specifically designed for low-voltage switchgear that is empty and without the internal components (such as circuit breakers, PLCs). The IEC standard mainly defines the mechanical properties of the electrical enclosure (IK rating, hinge mechanical strength), environmental protection levels, materials and safety.
However, it does not specify the electrical performance of internally installed equipment, does not apply to fully assembled switchgear, and does not specify wiring, protection coordination, or functional control logic.
ISO Standard for Electrical Enclosure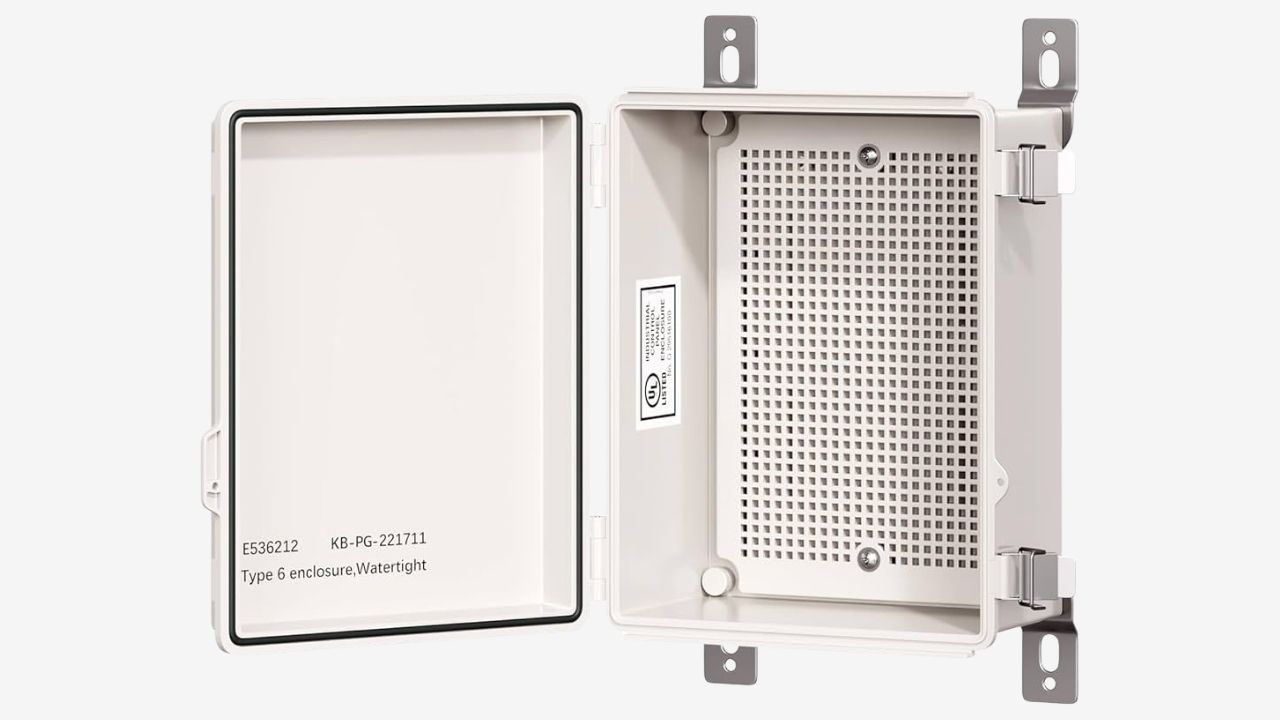
The ISO standard sets out the general design, safety and performance principles for electrical enclosures. It mainly focuses on environmental protection, mechanical integrity and material quality.
The ISO standard does not define the electrical safety or functional performance of the equipment inside the enclosure. It is usually used to support or complement the IEC standards, which are more specifically targeted at electrical installations.
NEMA & UL Standard for Electrical Enclosure(North American)
ال معيار NEMA and UL standard are usually used as application standards for the North American system. For products to be launched on the market, they usually need to obtain third-party safety certifications such as UL or CSA. For instance, the UL 50E standard is a legally binding product certification system.
Unlike the IP code system, the NEMA system has similarities but cannot be directly converted. The NEMA standard focuses more on the protection of the final application environment and contains specific safety requirements such as structural and material weather resistance. This is related to the strict product liability laws in the local area and the long-established engineering practices.
EN Standard for Electrical Enclosure(European Union)
In the EU market, the CE marking is a mandatory legal requirement. Manufacturers must verify that their products comply with the relevant EU directives. The core way to prove this is to meet the corresponding harmonized standards, such as EN IEC 62208 or the EN IEC 61439 series.
EN standard is the localization of international standards such as IEC. Its purpose is to eliminate trade technical barriers within the European Union.
Key point: IEC 60529 refers to technical classification, such as IP rating or IK rating. While UL 50E or EN IEC 62208 are product certifications. If you are exporting to North America, you need to obtain شهادة UL. If you want to export to the EU, you also need to complete the CE conformity procedure.
Comparison of Major Standards Systems
IP Rating vs NEMA Rating
IP and NEMA are common standards for your electrical enclosures. The core difference between them lies in that IP is an international technical testing grade, mainly focusing on dustproof and waterproof performance. While NEMA is a type of description for applications in North America, paying more attention to the usage environment and safety. The two cannot be directly equated.
IP mainly defines the protective capability of the enclosure against solid foreign objects and liquids, while NEMA describes the indoor and outdoor environments to which the enclosure is applicable, and includes more safety requirements.
The former is mainly for contact prevention, waterproof and dustproof, while the latter involves corrosion prevention, explosion prevention and oil immersion in addition to waterproof and dustproof. The former has globally unified and clear testing procedures and conditions. The latter is mostly performance descriptions and does not have publicly available, detailed unified testing procedures.
Key Technical Requirements for Standardization
The technical requirements for standardized electrical enclosures are designed to guarantee the safety, reliability and applicability of the enclosure throughout its lifecycle. The key technical requirements mainly cover the following core areas.
Fire and Explosion Protection
Material Flame Retardancy: According to standards such as IEC and UL, the flame retardant grade of non-metallic materials is evaluated. The main purpose is to prevent the material itself from becoming a source of fire or a fuel for combustion.
الحماية من الانفجار: For explosive environments, the enclosure must comply with the explosion-proof type specified by IEC or أتيكس.
It mainly aims to prevent internal electrical sparks or high temperatures from igniting the external environment. It has extremely high requirements for structural strength and control of joint surface gaps, and it must be able to withstand the pressure of an internal explosion.
Electrical Safety Requirements
Electrical Shock Protection: Specify insulation and grounding measures for live components. It also requires sufficient electrical clearance and creepage distance.
Insulation Requirements: Based on factors such as overvoltage categories, the minimum electrical clearance and creepage distance values are specified in the IEC standards. Guarantee that components at different potentials do not break down or leak electricity.
Leakage Current: The regulations for potential leakage currents are specified on the wires. This is to prevent the risk of the enclosure becoming electrified due to insulation failure.
Mechanical and Structural Requirements
مستوى الحماية: IP rating is verified through tests such as dust and water spray. IK code specifies the level of the enclosure’s resistance to mechanical impacts.
Mechanical Strength: Conduct tests such as hoisting and static load tests on the enclosure. Guarantee the structural integrity of the enclosure during transportation, installation and usage.
Materials and Processes: The standards specify the minimum thickness of the metal sheet, the types of layers, and the strength requirements for welding. This guarantees the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the base material.
Environmental Adaptability
Climate Adaptability: The standard stipulates the operating temperature range, humidity resistance, and UV resistance of the enclosure. It guarantees that the enclosure remains unchanged and keeps its performance under extreme temperatures and humidity conditions.
مقاومة التآكل: Conduct salt spray tests on the stainless steel enclosure or in cases where corrosion resistance is required. Evaluate the corrosion resistance of the enclosure.
Chemical Stability: Non-metallic materials need to undergo tolerance tests for common oils, solvents, cleaning agents, etc. Prevent material deterioration of the enclosure caused by daily maintenance or usage.
Standardization Challenges and Issues
Standard Lag: You will find that the development of intelligent technologies, new processes, and new materials far outpaces the cycle of standard updates. As a result, products can only be fitted with outdated standards that are no longer suitable.
The Contradiction between Customized Requirements and Standardization: For high-end equipment or special scenarios, you need to customize the enclosure. However, standardized products are difficult to meet unique performance, size, or integration requirements.
Certification Barriers: The costs and procedures for obtaining mandatory certifications in different markets are extremely high, making it a heavy burden for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Inconsistency in Conformity Determination: Different certification bodies or market supervision departments have different standards for inspecting the compliance with the standards, which affects market fairness.
What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing Standard Electrical Enclosures?
Compliance: First of all, you must verify whether the product has UL, CSA or CE certification, and clearly identify its IP or NEMA type.
Verify Authenticity: You also need to verify the authenticity of the certificate to prevent purchasing counterfeit products.
المواصفات الفنية: When purchasing an electrical enclosure, you must guarantee that the physical properties of the enclosure precisely match the actual application environment. Check whether the protection level, electrical enclosure size, materials, and cooling system are compatible with the usage environment and requirements.
Installation&Maintenance Convenience: You also need to check whether the enclosure has lifting points, a base, and whether the number, position and specification of the cable entry points are sufficient. Besides, you should also check if the vulnerable parts of the enclosure are easy to replace.
Which Standards Does Your Enclosure Need to Follow?
To understand this issue, you need to first clarify the following questions:
- Where is your target sales market? Or where is your product applied?
- Under what specific environmental conditions is your product exposed?
- What are the specific requirements of the project specifications or the client?
- What standards and certifications do the suppliers have?
Your target market determines the standards for the electrical enclosure. If you are applying in North America, it will be the UL standard. If your target market is in Europe, the enclosure must meet the CE marking requirements and also undergo a conformity assessment in accordance with the IEC standards.
The specific exposed position of the electrical enclosure determines the type of function you choose for the enclosure. For example, in an ordinary indoor environment, you can follow the general basic standards. In dusty, humid or outdoor environments, you need IP level protection. In explosion-hazardous areas, you need to select explosion-proof enclosures that comply with IEC or ATEX directives.
Besides, you need to review the enclosure specifications clearly stated in the design drawings and technical specifications. You can ask the supplier to provide a formal test report or certification certificate to verify whether the enclosure is qualified.
التعليمات
Which is More Suitable and Cost-Effective for Corrosive Environments, Stainless Steel or Engineering Plastic Enclosures?
Generally speaking, stainless steel is your preferred choice when the environment is subject to physical impact, high temperature, high structural strength or long life. Its long-term cost-effectiveness is higher.
When the corrosion is mainly composed of chloride ions, the environment is not impacted, insulation is needed, and you have budget requirements, engineering plastics are your preferred choice. Its initial cost advantage is more obvious.
The specific selection needs to be analyzed based on your specific usage environment and cost.
In Which Applications do You Need Special Functional Requirements such as Transparent Windows, Explosion-Proof Certification, and Electromagnetic Shielding?
The transparent window is mainly used in high-voltage switches or in situations requiring a solid state. The explosion-proof enclosure is used in explosive gas environments or dust environments. Electromagnetic shielding is mainly applied to high-precision electronic equipment, high-voltage switchgear, or military equipment. In practical applications, the electrical enclosure you purchase may simultaneously meet multiple requirements.
Is the Certification Claimed by the Product for the Entire Enclosure or only for Certain Components?
This depends on the type of certification. Common performance standards such as IP and NEMA are designed to test the entire enclosure directly. Explosion-proof certification not only covers the overall structure of the enclosure but also needs to explicitly cover the material and thickness of the observation window, sealing gaskets, and every other key component. Any change to any component may lead to the invalidation of the certification.
Final Thought
KDM is a professional manufacturer of custom electrical enclosures. Our products have obtained IP and NEMA performance certifications. Moreover, we also have UL, CE, and other certifications. We can offer standardized enclosures as well as professional customization services for you. As an experienced manufacturer, we have collaborated with many international renowned brands. اتصل بنا to get your product customization plan.



